 |
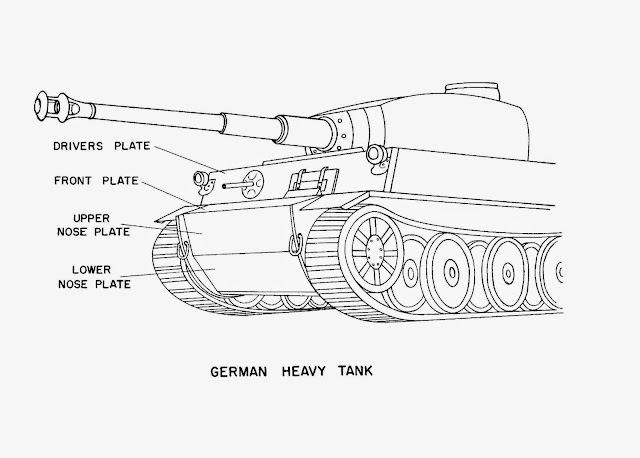
| “German heavy tank”, Tactical and Technical Trends #20, March 11th, 1943. |
Monday 31 October 2022
Tiger Killers
Friday 28 October 2022
Borgward Tankettes
"Main Intelligence Directorate of the Red Army
October 20th, 1943
#200558ss
Moscow
To the Commander of the Armoured and Mechanized Forces of the Red Army, Colonel General of the Armed Forces, comrade Fedorenko
Agents report (still need to be confirmed) that the Germans are producing B-4 tankettes that are controlled by radio and are conducting training on their use.
The tank is loaded with 300 kg of explosives and has several smoke emitting devices. It is designed for destruction of bunkers, making passages through obstacles, and clearing minefields.
Wednesday 26 October 2022
Tanks at Khalkhin-Gol
"To the Chief of the RKKA ABTU
August 19th, 1939
Directorate of the People's Commissar, 1st Department
#755895ss
On orders of the Deputy People's Commissar of Defense, Army Commander 1st Class comrade Kulik, I send you a copy of the act on the inspection of combat and training in the 1st Army Group for your inspection and execution of necessary measures.
Deputy Chief of the 1st Department,
Major Bibikov
Act [to certify that] I conducted an inspection of the combat and training in the 1st Army Group fighting in the region of Khalkhin-Gol during the period of July 11th-24th, 1939
1. Permanent units
[...]
Armoured units:
The 7th, 8th, and 9th Armoured Brigades are essentially armoured cavalry, more suitable for guarding borders and internal security. They did not train to fight alongside infantry and don't know how to do this. These units played a big role in the initial stages, but took heavy losses. The arrival of poorly trained reinforcements weakened them, they need to train and re-equip.
Monday 24 October 2022
Ever-Changing Tank Nomenclature
One of the topics that resurfaces in arguments about armoured vehicles is classification. It wouldn’t be so bad if people far from the science of armoured vehicles made mistakes, but quite notable historians also throw fuel on the fire. The T-28 is one of the most misunderstood vehicles. There is a certain group of people who draw modernisations onto the T-28 that would allegedly make it a suitable replacement for the T-34. After all, both have a 76 mm gun, similar weight, two tracks, basically the same thing! The fact that the T-34 was built to replace the BT doesn’t bother them, neither does the fact that it was the SMK that was first supposed to replace the T-28 and then the KV. The T-28 tank was included in heavy tank brigades. This seems like a very strange fact if one is not familiar with the Red Army’s system of classifications. Similar mistakes are made regarding tanks of other nations. For instance, the Panther is often called a heavy tank, but it’s enough to look at where these tanks went and what vehicles they replaced. Today we will cover the Soviet tank classifications, touching foreign vehicles a little for context. Keep in mind that the same names can mean different things in different times.
 |
Classification of tanks in the Red Army. Bronevoye Delo magazine, March 1921. |
 |
| A 16 ton maneuver tank designed by the GUVP. No one ever called this tank "medium". |
Friday 21 October 2022
Polish Tank Destroyer
The growth of tactical-technical requirements is a normal phenomenon for any army in the world. The brass also often doesn't know when to stop, which results in a strange metamorphosis. This happened to the tankette class of vehicles. Initially, the concept was something akin a mobile machine gun nest: a machine gun with a shield, engine, and tracks. Early tankettes were one-man vehicles, but experiments in the early 1920s showed that you need at least two crewmen. The Carden-Loyd Mk.VI is a classic example of this concept. Nevertheless, many nations quickly started treating it as a tank, albeit a small one. Requirements for these tankettes grew until they were more suited to tanks, and so the tankette withered away.
 |
| TK-S tank destroyer, a great example of a successful modernization of an obsolete vehicle. |
Wednesday 19 October 2022
Video: 6-pounder and 57 mm M1 Gun in the USSR
Both British made 6-pounders and American made 57 mm M1 guns were shipped to the USSR in various forms, but one was received much better than the other. I talk about why in my latest video. Huge thanks to Major (Ret.) Michael Calnan, the Swords and Plowshares Museum, and the 1st Canadian Parachute Battalion and 191st Rifle Division reenactment groups for the footage used in this video.
Monday 17 October 2022
The Main Soviet Pre-War Tank
Friday 14 October 2022
DShK vs Pz.Kpfw.IV
"Results of firing the 12.7 mm DShK machine gun with the B-32 bullet against the German Pz.Kpfw.IV tank
|
Range |
Hit location |
Armour slope from vertical |
Total angle (slope + shooting angle) |
Armour thickness |
Hits |
Results |
|
100 m |
Right side of the turret |
25 deg |
70 deg |
20 mm |
5 |
15 mm deep impacts (1 on photo #63) |
|
50 |
25 |
90 |
20 |
2 |
18 mm deep impacts (2 on photo #63) |
|
|
100 |
Right side of the hull, engine compartment |
0 |
70 |
20 |
3 |
Complete penetration |
|
100 |
Turret rear |
12 |
90 |
20 |
5 |
One complete penetration, 4 18 mm deep dents |
|
100 |
Hull rear |
0 |
70 |
20 |
2 |
Complete penetration |
|
150 |
0 |
70 |
20 |
2 |
17 mm deep dents |
|
|
150 |
0 |
90 |
20 |
2 |
18 mm deep dents |
Wednesday 12 October 2022
Artillery vs Fortifications
"To the Military Council of the 16th Army
1. Experimental trials using an anti-tank rifle, 45 mm gun, and 76 mm gun were performed against an earth and timber bunker on July 31st, 1942.
The size of the bunker was 5.5 by 5.5, the thickness of the walls was 1.4 meters, formed by two log frames. The space in between was filled with earth and logs.
Results of firing from 300 meters:
- 76 mm regimental gun:
- HE grenade fused for explosive effect: the outer log frame is destroyed with one grenade. 5-7 direct hits are needed for complete destruction.
- Shrapnel with impact fuse: wall of the bunker is penetrated fully, shell explodes inside the bunker.
- 45 mm gun AP shell: penetrates both the front and rear walls of the bunker.
- Anti-tank rifle: at 100-200 meters the bullet penetrates one wall of the bunker. The bullet maintains enough energy to kill.
Monday 10 October 2022
Heavy Guns vs KV-1
"XXXVIII Army Corps HW
Operational Department
Lempelevo, September 19th, 1941
RE: Experimental firing by Pz.Jg.Abt.563 against a Russian 52 ton tank (not reinforced).
1 diagram
18th Army HQ
Attached is the result of experimental firing against a Russian 52 ton tank (not reinforced) ordered by the corps HQ.
- Gun: l.F.H.18
- Ammunition: 10 cm Gr.39 rot (5th charge)
- Range: 200 m
- Results:
- 1st shot to the side destroyed the road wheels.
- 2nd shot to the turret ring jammed the turret. No penetration.
- 3rd shot to the turret ring jammed the turret. No penetration.
- 4th shot to the turret side penetrated about 5 cm, no complete penetration.
Friday 7 October 2022
Deliveries
"Table of arrivals of tanks at the front lines in 1941, by type
|
Type |
Domestic |
British |
American |
Total |
||||||
|
Month |
KV |
T-34 |
T-60 |
T-70 |
Mk.II |
Mk.III |
Mk.IV |
M3 S |
M3 L |
|
|
Total 1941 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20,740 |
|
Jan |
126 |
206 |
348 |
- |
- |
16 |
- |
- |
- |
696 |
|
Feb |
165 |
420 |
260 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
845 |
|
Mar |
105 |
338 |
84 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
527 |
|
Apr |
320 |
702 |
576 |
- |
134 |
144 |
- |
14 |
32 |
1922 |
|
May |
350 |
1003 |
898 |
- |
255 |
171 |
- |
30 |
16 |
2723 |
|
Jun |
199 |
698 |
657 |
103 |
- |
74 |
- |
144 |
222 |
2091 |
|
Jul |
299 |
1177 |
746 |
371 |
86 |
44 |
- |
66 |
91 |
2880 |
|
Aug |
178 |
1378 |
250 |
583 |
10 |
63 |
- |
35 |
98 |
2595 |
|
Sep |
45 |
598 |
- |
439 |
- |
72 |
- |
54 |
43 |
1251 |
|
Oct |
160 |
1100 |
75 |
640 |
- |
10 |
- |
24 |
5 |
2024 |
|
Nov |
215 |
1312 |
- |
838 |
85 |
163 |
- |
187 |
61 |
2861 |
|
Dec |
239 |
1678 |
48 |
1026 |
- |
- |
42 |
23 |
16 |
3072 |
|
Total 1942 |
Total domestic: 20,957 |
Total foreign: 2530 |
23,487 |
|||||||
This data is interesting on its own, but it's also interesting to compare to deliveries of foreign tanks. The first Matilda and Valentine tanks began arriving during the Battle for Moscow and were thrown into battle with little preparation. As you can see in the above table, once the situation stabilized a little bit it took some time before new units with British tanks could be properly outfitted. Large deployments of Matildas and Valentines only take place in April, four months after deliveries began.
A similar picture can be seen with American tanks. The first shipments arrived in January of 1942 and we start seeing a small number of these tanks on the battlefield in April-May, 4-5 months later. Once the pipeline was set up, it was not as hard to deploy new tanks. A bump shipments that came in May hits the front lines in June. A lot of tanks were tied up in delivery by the end of the year: 3875 foreign tanks were delivered to the USSR in 1941-1942, but only 2530 were actually fielded before the end of 1942.
You can see the same pattern with Soviet tanks. Evacuation of factory #183, the USSR's largest producer of the T-34 tank, began in September of 1941. The factory began to set up in the Urals in December-January, and by May of 1941 you see a spike in deliveries of T-34 tanks. Similarly, production of the T-70 was authorized in March of 1942 and we see these tanks begin to arrive on the front lines in July.